TAMS / Java / Hades / applets (print version): contents | previous | nextsimple counter
 DescriptionThis applet is the first in a series of applets that
demonstrate simple finite state-machines (FSM)
realized with the Hades interactive state-machine editor,
called JavaFSM.
DescriptionThis applet is the first in a series of applets that
demonstrate simple finite state-machines (FSM)
realized with the Hades interactive state-machine editor,
called JavaFSM.
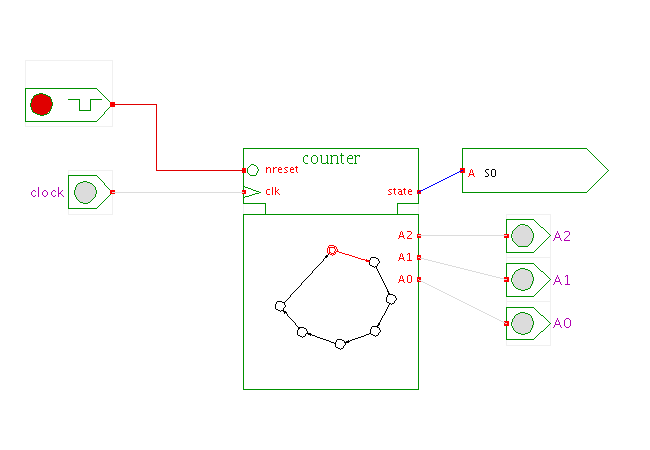
The state machine shown here is a simple counter with seven states,
named S0, S1, S2, ..., S6 which
correspond to the counter values (zero, one, two, ..., six).
Naturally, any number of states could have been chosen instead of seven.
Every state machine realized with the JavaFSM editor
includes a clock input
and an asynchronous reset input, as well as a default 'state' output.
A rising edge of the clock input will trigger a state transition,
while a low level on the reset input resets the state machine to its
starting state (defined in the machine description).
The 'state' output transmits a string value with the name of the
current state of the state machine.
Any number of additional inputs and outputs can be defined in the
state machine editor.
The basic counter shown here has no additional inputs,
but uses three outputs called (A2,A1,A0) to transmit the binary encoded
counter value.
Standard Hades components can be connected to those inputs and outputs.
Note that the graphical symbol for the state machine
shows an interactive miniature version of the FSM,
highlighting the current state and the currently active transition.
Click the 'clock' and 'reset' input switches, or type the 'c' and 'r'
bindkeys to control the simulation and watch the counting process.
To edit the state machine, activate the popup-menu on the
FSM symbol and select the edit menu item.
This opens the editor window for the FSM,
which uses a mode-oriented user-interface.
- move-mode: Click-and-drag any one of the state
symbols (circles) to a new location on the editor canvas.
The currently selected state is highlighted in red.
Use the textfield on the lower left to set the name
of the selected state.
To change the output values for Moore-type outputs in the selected state,
first select that output in the list on the lower left and then
select the new output-value (0 or 1) in the radio-button on the
bottom.
- state-mode: Click the mouse to create a new state
and set its name and the default output values via the GUI controls
on the lower left part of the editor window.
- transition-mode: To create a new transition between states,
first click of the initial state, then on the final state.
Enter the logical condition that activates the transition
in the textfield on the lower left, e.g. "*" for an always active
transition, or "A&B" for a transition that is only active if
the "A" and "B" inputs are both active (1).
- comment-mode: Click the mouse to specify the position for
a new text comment on the editor canvas; next enter the comment
into the text-area in the lower left part of the editor window
and finally press "apply" to create the comment.
- delete-mode: Click the mouse to delete a state,
transition, or comment.
- starting state-mode: Click the mouse on a state symbol
to select that state as the initial starting-state of the FSM.
- Click the test FSM button to run a simple selftest that
checks for each state whether transitions are active for any
combination of inputs.
- Use the load and save as operations to load or save
the FSM design file.
-
Due to a bug, the name of the FSM design file (.fsm) is not currently
saved in the embedding Hades design file (.hds).
Please open the .hds file in your favorite text editor,
search for the FsmWrapper component(s),
and manually enter the .fsm file name instead of the 'null' value.
For detailed documentation of the JavaFSM editor,
please visit its
home page.
Run the applet | Run the editor (via Webstart)
Impressum | 24.11.06
http://tams.informatik.uni-hamburg.de/applets/hades/webdemos/45-misc/05-fsm-editor/counter_print.html
 DescriptionThis applet is the first in a series of applets that
demonstrate simple finite state-machines (FSM)
realized with the Hades interactive state-machine editor,
called JavaFSM.
DescriptionThis applet is the first in a series of applets that
demonstrate simple finite state-machines (FSM)
realized with the Hades interactive state-machine editor,
called JavaFSM.