
 |  |
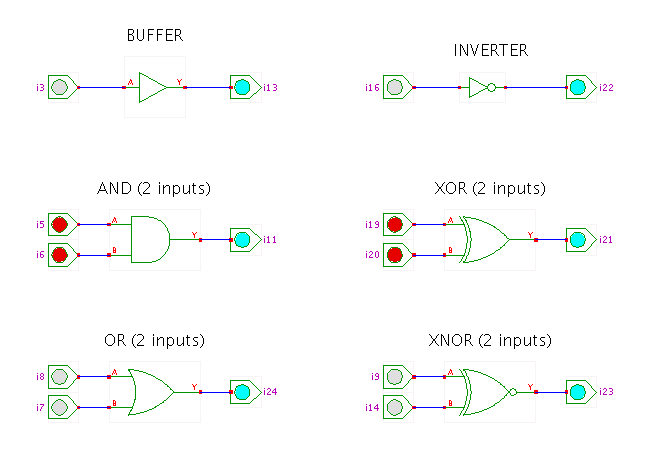 DescriptionA demonstration of the XOR and XNOR gates.
Click the input switches to toggle the corresponding input value
between 0 and 1, and watch the resulting behaviour.
You can also use shift+click to toggle the input value between
the states 0, 1, Z (tri-state, not driven) and X (undefined).
Alternatively, type the indicated bindkeys (a,b,s,d,f,g,w,e,r,t)
to control the switches.
DescriptionA demonstration of the XOR and XNOR gates.
Click the input switches to toggle the corresponding input value
between 0 and 1, and watch the resulting behaviour.
You can also use shift+click to toggle the input value between
the states 0, 1, Z (tri-state, not driven) and X (undefined).
Alternatively, type the indicated bindkeys (a,b,s,d,f,g,w,e,r,t)
to control the switches.
Note that two different interpretations exist for the concept of a 'multiple-input' XOR gate. First, the 'either A or B or C or ...' interpretation means 'exactly one of the inputs is true'. The second interpretation constructs a multiple-input XOR gates from a cascade (chain/tree) of two-input XOR gates, which corresponds to the parity of the input values.
For example: The following table shows the truth-table of the different gates for three inputs:
C B A 1-of-3 even-parity odd-parity 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 1
For a demonstration of the parity interpretation,
see the parity generator applets at
and
.